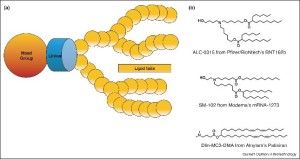
mRNA lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) have recently been successfully proposed as vaccine against SARS-CoV-2, although the research and development began decades ago. The main advantages of these nanovectors are their easily production and modularity according to different needs. The mRNA or messenger RNA, loaded within them, is a chain of nucleotides consisting of a phosphate molecule, a nitrogen base and a sugar. The mRNA is essential for every form of life because it is responsible for the transmission of important information to cells. When designing a mRNA-LNP vaccine, it is crucial to optimize the formulation in terms of effectiveness, stability and safety. The nucleotides of the mRNA sequence can be modified to increase protein expression, make it more stable and prevent the immune system recognizes it as non-self and degrades it.
Lipid nanoparticles are the envelope that protects and allows the mRNA to reach its destination. They generally made up of lipids, cholesterol and a polymer, PEG. The ionizable lipids are the most used components and are formed by carbon chains, an ionizable head and a linker that connects these two units. PEG, on the other hand, has the function of avoiding the aggregation of nanoparticles, thus improving the stability of the formulation.
Other strategies to increase the long-term preservation and allow large-scale production can be -80 degrees preservation or freeze-drying. Obviously these are some of the multiple considerations that must take into account during the development of a mRNA vaccine. As the authors say, there is no unique recipe for an effective nanovector, but the synthesis must be optimized considering the therapeutic purpose.
Link to full article: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0958166921001932