In order to allow Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS) to become an important tool for the biochemical research, there is still the need for an effective and reliable SERS substrate able to enhance signal from a broad range of samples.
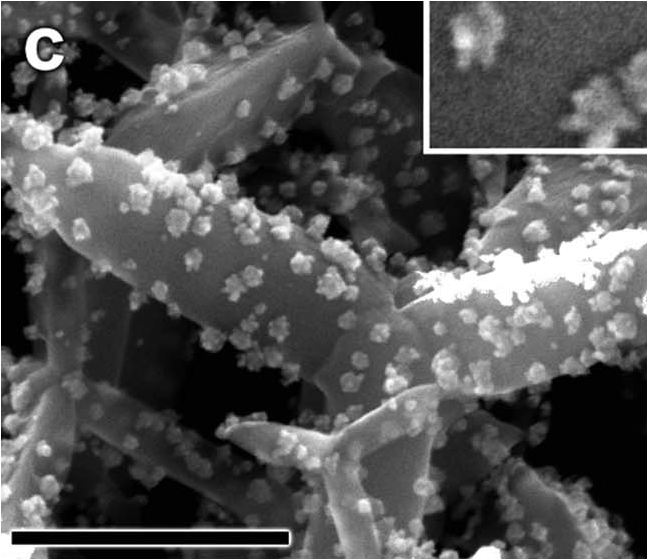
To respond to this necessity Labion in collaboration with the signal group of IMEM-CNR developed a new 3D SERS substrated made of branched gold nanoparticles supported on a network of micrometric ZnO tetrapods. The obtained SERS substrate material is characterized by good enhancing properties, a good reprodcibility of the signal and an excellent stability of the performace in time.
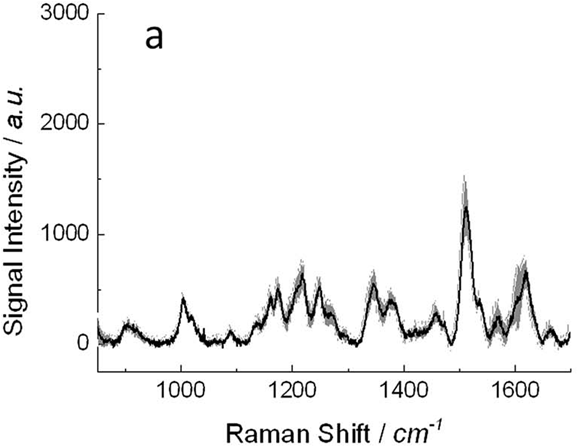
Thanks to this material we demonstrated how it is possible to quickly detect apomorphine (a drug used for the managment of Parkinson’s disease) at micromolar concentration potetially allowing to subministrate the right amount of drug each patient in the framework of a more personalized medicine.
The results of this studies have been recently published on RSC Advances:
S. Picciolini, N. Castagnetti, R. Vanna, D. Mehn, M. Bedoni, F. Gramatica, M. Villani, D. Calestani, M. Pavesi, L. Lazzarini, A. Zappettini and C. Morasso “Branched gold nanoparticles on ZnO 3D architecture as biomedical SERS sensors” RSC Advances, 2015, 5, 93644-93651.